What are the functions of proteins in the body – Proteins, made up of chains of amino acids, are the main components of cells. They are important for cell structure, metabolism, and other cellular processes. Proteins can also bind to other molecules or cells to form protein complexes.
Have you ever wondered what are the functions of proteins in the body? We are all familiar with the basic functions of proteins – they make up muscles, hair, skin, bones, and other body structures. However, proteins are also important in other processes, such as immunity, digestion, metabolism, and aging. So what exactly are they?
Learn the basics of proteins and their bodily functions in this post. We will discuss their roles in immunity, digestion, metabolism, and aging.
Helping make enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. Enzymes help our bodies break down food, regulate the pH of our blood, and produce energy from glucose.
A large portion of enzymes are made in our liver. This is a very complex organ that performs many functions.
Many know enzymes as the active components in our digestive system that break down food. Enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller molecules our bodies can absorb.
There are over 5,000 different types of enzymes. They are named based on their function. Here is an example of an enzyme that breaks down glucose into sugar.
Helping make antibodies
Antibodies are protein molecules that defend us against infections. They help us fight viruses, bacteria, and other microbes. Antibodies are also key to the functioning of the immune system. They attack microbes that invade our bodies and help us identify and destroy infected cells.
Antibodies are made by white blood cells called B-cells, part of the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes are found throughout the body and contain many different types of white blood cells. These nodes help the immune system distinguish between healthy and unhealthy cells. When an antibody encounters an antigen (a substance that triggers an immune response), it binds to the antigen and marks it for destruction.
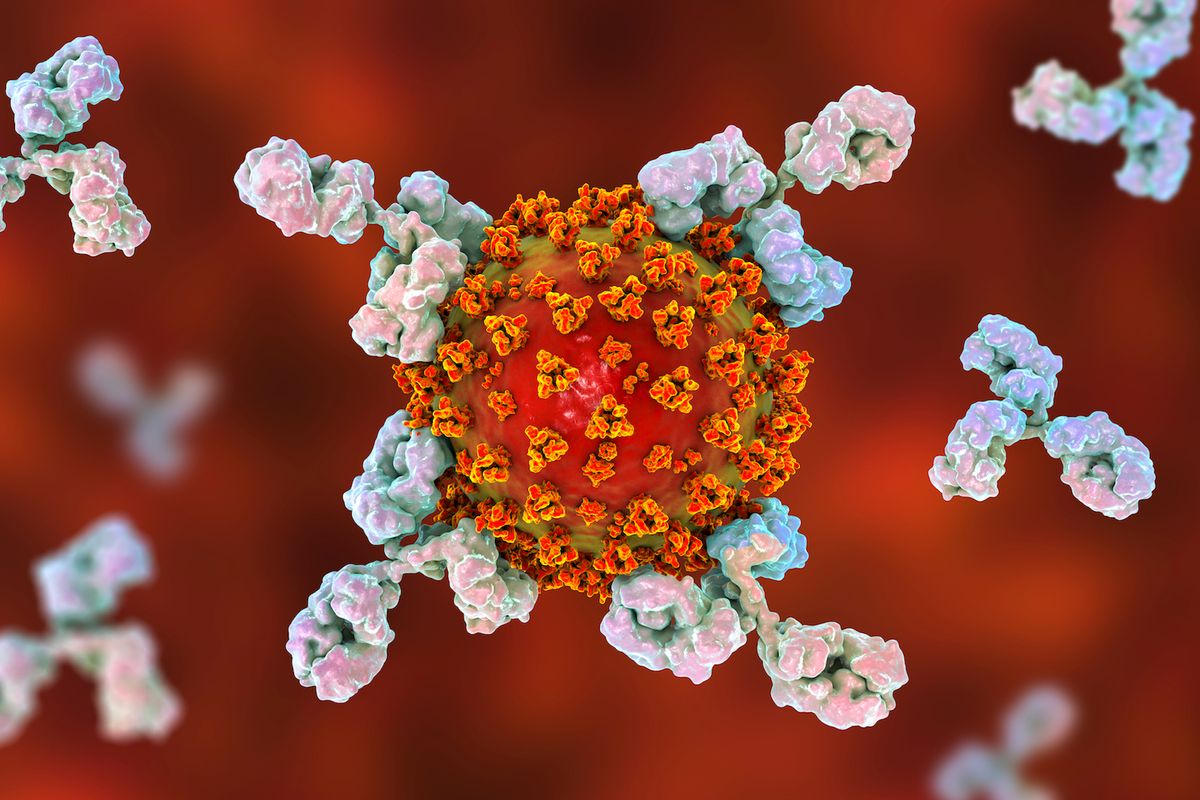
Antibodies can recognize antigens from various organisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. But they effectively fight off bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
Helping build bones
You already know that proteins are found in the human body’s cells, tissues, and organs. Proteins are responsible for making us look and feel healthy. They are also vital for maintaining the structure and function of the body.
As we grow older, we lose our ability to produce new proteins, weakening bones. As a result, fractures become more common.
There are some ways that you can help build bones. We’ll discuss the role of protein in bone growth, how protein deficiency can lead to bone loss, and some tips to help prevent bone loss.
Helping to protect cells
Proteins are the most abundant type of biomolecules in our body. They are essential for life, and their bodily functions are vital. Here, we discuss the different types of proteins, their functions, and how they can help protect the human body.
What Are Proteins? Proteins are composed of amino acids that make up the majority of living organisms.
There are 20 different amino acids, but only ten are used to build proteins. These ten amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and the rest are called non-essential amino acids.
Essential Amino Acids The crucial amino acids are required for the body’s survival. They are indispensable for growth and development and are also the building blocks of proteins.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between natural and high-protein diets?
A: A natural diet is when you eat foods that come from nature. Eating meat, eggs, or protein powder is A high-protein diet.
Q: What is a good diet for someone who wants to lose weight?
A: A good diet for a person who wants to lose weight has lots of vegetables and fruit and no processed foods.
Q: What do proteins do in the body?
A: Proteins are used in various ways to help the body grow, maintain its structure, and perform its basic functions. Proteins are very important to keep the body healthy and functioning.
Q: What is the difference between muscle proteins and non-muscle proteins?
A: Non-muscle proteins include enzymes, structural proteins, hormones, and antibodies. These are all used to carry out a variety of tasks.
Q: How does muscle protein work?
A: The muscle proteins help to move and change other molecules inside the cell, which helps to regulate different body activities.
Q: What are the functions of proteins?
A: Proteins are the building blocks of our bodies. They help keep us alive and healthy by supporting us to be strong and flexible. They also control how our bodies function. They make up all our organs and the fluids inside them.
Q: Where do proteins come from?
A: Proteins are made by living things called cells. A cell contains a mixture of organic chemicals. Some of these chemicals become proteins.
Myths About the functions of proteins
1. Proteins are the building blocks of the human body.
2. Proteins make up enzymes and hormones.
3. Proteins help the body fight off disease.
4. The functions of proteins are to build the body’s structure.
5. The function of proteins is to carry nutrients throughout the body.
Conclusion
The human body is made up of various cells. There are three major cell types: epithelial, blood, and muscle. Each cell has different functions. It must communicate with other cells and the outside environment to perform its tasks. This is done through the exchange of small molecules called ligands. Ligands are chemical compounds that allow cells to communicate with each other.
Each cell type has specific ligands that allow them to interact with other cells. Other ligands control how many cells interact with each other and their environment. Some ligands are produced by cells, while others are produced externally. Proteins are among the external ligands. They are macromolecules that contain a chain of amino acids.
Proteins are made up of 20 different amino acids. They can be either soluble or insoluble. Soluble proteins can pass through the cell membrane easily. Insoluble proteins require the help of enzymes to cross the membrane.


